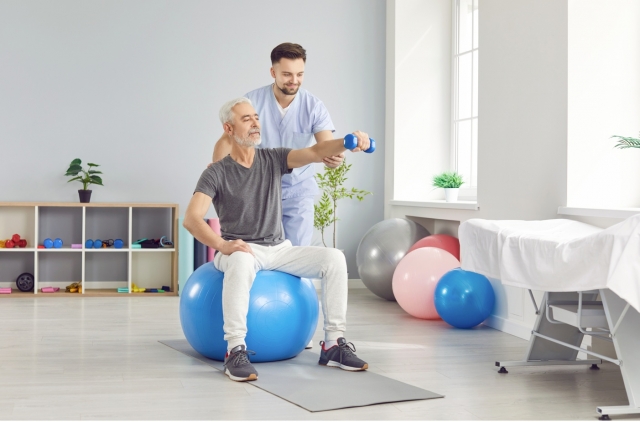
As you grow older, staying active becomes a key to living a vibrant, independent life. Whether it's gardening, hiking, dancing, or simply walking to the store, staying on the move keeps us healthy and happy.
But aging can bring challenges like stiff joints, weaker muscles, or even the fear of falling. That's where physical therapy comes in. Physical therapy for active aging is like a trusted guide, helping older adults keep their strength, balance, and confidence to maintain their quality of life.
In this article, you'll learn how physical therapy works to support active aging, breaking it down into simple steps that anyone can understand.
Step 1: Getting to Know You
The journey begins with a conversation. When you visit a physical therapist, they start by learning about you. They'll ask about your health, lifestyle, and goals. Do you want to walk longer distances? Play tennis again? Or maybe just climb stairs without pain? They'll also check how you move. They'll watch how you walk, test your strength, and see how well you balance. If you have pain or specific conditions like arthritis, they'll take note of that, too.
This step is crucial because everyone's body and goals are different. For example, a 70-year-old who loves swimming will need a different plan than someone who wants to garden without back pain. By understanding your unique needs, the therapist creates a plan that's just right for you. This personalized approach ensures that every exercise or technique is designed to help you thrive.
Step 2: Keeping Your Joints and Muscles Flexible
One of the first things physical therapy focuses on is keeping your body flexible. As you age, joints can get stiff, making it harder to bend, reach, or move freely. Imagine trying to tie your shoes when your knees feel creaky. That's where flexibility comes in.
During a physical therapy session, physical therapists use gentle stretches and exercises to loosen up your joints and muscles. For instance, they might guide you through stretches for your hips or shoulders, helping you move more easily. These exercises aren't just done in the clinic because you'll also learn simple stretches to do at home.
Over time, this increased flexibility makes everyday tasks like getting out of a chair or reaching for a shelf feel smoother. Plus, it helps you stay active in fun ways, like dancing or playing golf, without feeling stuck.
Step 3: Building Strength for a Stronger You
Another key part of physical therapy is building strength. As you age, your muscles naturally lose some of their power, a process called sarcopenia. Weaker muscles can make it harder to carry groceries, climb hills, or even stand up from a low chair.
Physical therapy fights this by including strength-building exercises tailored to your needs. You won't be lifting heavy weights like a bodybuilder, though. Instead, therapists use exercises like leg lifts, resistance bands, or even your own body weight to build muscle.
For example, practicing sit-to-stand movements strengthens your legs, making daily tasks easier. Stronger muscles also support your joints, reducing pain from conditions like arthritis.
Step 4: Mastering Balance to Stay Safe
Falls are a big concern when aging, but physical therapy can help you stay steady on your feet. Balance exercises are fundamental to active aging programs, incorporating activities such as single-leg stands, heel-to-toe walking, or balance board use. The therapist might also have you practice stepping over small obstacles to mimic real-life situations.
It's important because good balance reduces the chance of falling, which can lead to serious injuries like broken bones. It also boosts your confidence, so you're not afraid to move around. Over time, balance training helps you feel more in control, whether you're navigating a crowded sidewalk or dancing at a family party. It's like giving your body a built-in safety net.
Step 5: Easing Pain to Keep You Moving
Pain can be a major roadblock to staying active. Whether it's from arthritis, an old injury, or sore muscles, discomfort can make you want to sit still. Physical therapy offers ways to manage pain without relying only on medication. Therapists might use hands-on techniques, like massage or joint mobilization, to ease tightness. They could also apply heat or cold packs to soothe sore spots.
In addition, they'll teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around painful areas, which can reduce strain. For example, if you have knee pain, strengthening your thigh muscles can take pressure off the joint. By addressing pain, physical therapy helps you get back to doing what you love, whether it's walking in the park or gardening.

Step 6: Learning Smart Ways to Move
Physical therapy isn't just about exercises—it's also about learning how to move smarter. Therapists teach you the best ways to do everyday tasks to avoid strain or injury. For example, they might show you how to bend your knees when picking something up or how to sit with good posture to prevent back pain.
They'll also give you tips for your home, like using a sturdy chair for support during exercises or removing tripping hazards. These small changes make a big difference in keeping you safe and active. It's like learning the rules of the road for your body so you can keep going without hitting bumps.
Step 7: Boosting Heart Health and Stamina
Staying active isn't just about strength and balance—it's also about having the energy to keep up. Physical therapy treatment plans often includes low-impact activities like walking, cycling, or water exercises to improve your heart health and stamina. These exercises are gentle on your joints but powerful for your overall health.
For example, a therapist might design a walking program that starts slow and builds up over time. This boosts your endurance, so you can enjoy longer outings without feeling tired. A stronger heart also supports your mental health condition, as physical activity releases feel-good chemicals in your brain. It's a win-win for your body and mind.
Step 8: Tailoring Therapy for Chronic Conditions
Many older adults live with conditions like osteoporosis, diabetes, or heart disease. Physical therapy can be customized to manage these challenges while keeping you active. For instance, if you have osteoporosis, a therapist might focus on therapeutic exercises to strengthen your bones and improve posture. If you have diabetes, they might include activities to boost circulation.
This tailored approach ensures that therapy fits your health needs, making it safe and effective. It's like having a roadmap that guides you around obstacles so you can keep moving forward.
Getting Started with Physical Therapy
If you're curious about physical therapy for active aging, talk to your doctor or contact a local clinic. They can connect you with a licensed physical therapist who specializes in older adults. Bring your goals and questions to your first visit, and don't be afraid to share what you want to achieve.
In the end, physical therapy for active aging is about celebrating what your body can do and giving it the tools to keep going. It's a way to embrace aging with strength, confidence, and joy.