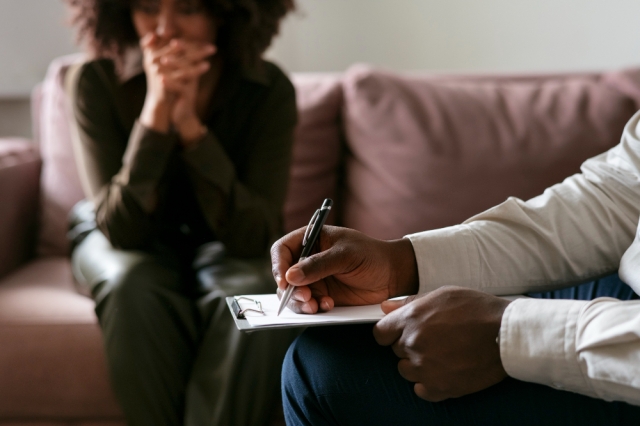
Addiction is a complex disease that affects the brain and behavior. While there are many different treatments available, therapy plays a critical role in helping people overcome addiction issues and maintain long-term recovery.
Understanding Addiction
Addiction changes the way the brain works over time. People suffering from addiction compulsively seek out drugs, alcohol, or behaviors like gambling, despite negative consequences. These substances and behaviors cause a rush of dopamine in the brain's reward system, leading to temporary feelings of pleasure or relief. Over time, the brain begins to associate the substance or behavior with feeling good, making it difficult to stop. Even after a person recognizes their addiction is causing harm, the cravings and impulses can be extremely challenging to overcome. This is why therapy is so important.
The Benefits of Therapy
Therapy provides tools and support for managing addiction in several key ways:
Exploring underlying issues
Therapists help clients identify core issues or experiences that may be contributing to addiction problems. Unresolved trauma, chronic stress, mental health issues, and social factors often play a role. Therapy allows people to process these root causes.
Building coping skills
Addiction often involves avoiding life's problems or difficult emotions through substance use. Therapists teach healthy coping mechanisms like meditation, journaling, exercise, communication skills, and more. Coping skills help clients navigate cravings, stress, and emotional triggers in recovery.
Changing behaviors
Therapists work with clients to identify addictive behavioral patterns and replace them with positive habits. Examples include joining a support group, engaging in new hobbies, setting healthy boundaries, and replacing addictive rituals with constructive routines.
Providing motivation
The road to recovery is long and challenging. Therapists offer empathy, encouragement, and accountability to help reinforce clients' motivation for change. Ongoing therapy helps deter relapse during vulnerable times.
Types of Therapy
Common therapeutic approaches for treating addiction include:
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Focuses on identifying unhealthy thought and behavior patterns and developing new skills. CBT helps manage cravings and change addictive behaviors over time.
Motivational interviewing
Seeks to enhance clients' internal motivation for change. The therapist expresses empathy and asks open-ended questions to explore ambivalence.
Group therapy
Brings together peers struggling with the same addiction. Members provide understanding and share strategies for overcoming addiction. The group dynamic in intensive outpatient treatment programs promotes accountability.
Family therapy
Involves family members affected by a loved one's addiction. It helps rebuild trust and communication patterns that support recovery.
Continued Support Through Recovery
Battling addiction requires an ongoing effort. Therapy empowers people to take control of addictive behaviors and build fulfilling lives in recovery. By providing professional guidance tailored to each client's needs, therapists help individuals overcome addiction one day at a time. Consistent therapy enables people to process their journeys, find meaning in life beyond addiction, and stay continually motivated to achieve lasting sobriety.
In addition to formal therapy, many find informal support groups helpful. Self-help groups like Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous provide mentoring and a compassionate community. Peer support helps normalize the recovery journey. Social connection is invaluable when overcoming addiction issues. Support groups are free to join and offer regularly scheduled meetings nationwide. Though not a substitute for professional treatment, the camaraderie of peer support groups reinforces essential tools that make long-term recovery possible.