Solar land lease firms play a crucial role in connecting landowners with clean energy producers in the rapidly evolving renewable energy sector. This blog explores the key aspects of working with solar land lease providers, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and maximize your asset's potential.
Key Considerations Before Signing a Solar Land Lease
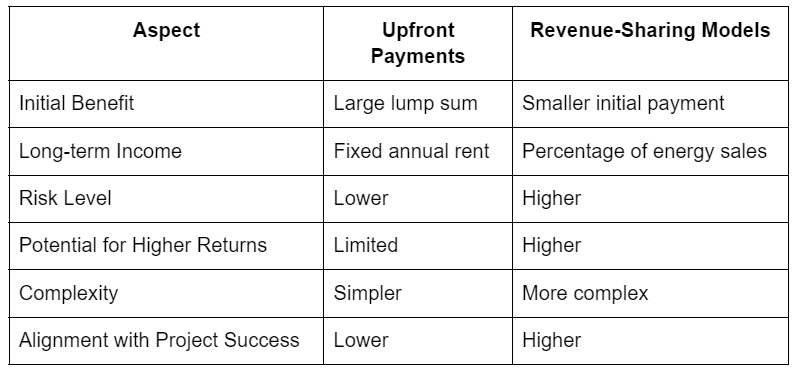
Before signing a contract, it's essential to understand the financial and legal implications of leasing your land for solar energy panels. It's important to understand different lease plans, such as upfront payments versus revenue-sharing schemes, and weigh the risks against potential long-term income.
You must stay aware of changes in the local and national solar energy markets as these can have a lasting impact on leasing prices. Navigating the legal system is equally important.
Technical Requirements and Site Evaluation
Solar companies will assess the suitability of your land for solar development. Understanding these requirements can help you gauge your property's potential value. Closer proximity to the grid increases the land's appeal for solar power plants by lowering connectivity costs and easing logistical issues.
Easy access to the road for building and continuous upkeep also raise the value of your land in the eyes of potential solar developers. To determine if solar energy projects are feasible and to optimize your land's value, you must understand these site-specific factors.
Your land's suitability and value to solar companies looking for land to lease can be greatly impacted by several important aspects when evaluating it for solar development. Flat terrain with slopes of fewer than five degrees is preferred because it reduces construction issues and increases the efficiency of solar panels.
Optimal sites for energy production are those with ample sunlight and minimal shade. The quality of the soil also plays a crucial role as it influences installation methods and costs. Additionally, proximity to existing infrastructure, particularly electricity grids, is essential for efficient operations and connectivity.
Negotiation Strategies for Maximizing Lease Value
Armed with knowledge about your land's potential, you can enter negotiations with confidence. Here are some strategies to help maximize your lease value:
Several significant factors should guide your conversation when negotiating lease terms for solar development on your property. Start by thinking about how long a lease should be optimally extended, balancing long-term security with the ability to adjust to shifting market conditions.
To ensure the lease remains financially viable over time, it is essential to arrange for annual rent escalations to account for inflation and market fluctuations. To ensure continuity and stability, discuss renewal alternatives up front and lay out the parameters for any prospective extensions or renewals.
Environmental effects are just as important as budgetary ones. Describe the project's impact on local ecosystems and species, and ensure that suitable mitigation measures are in place. Think about using the project to further the interests of the community by negotiating for upgrades or organizing initiatives to create jobs locally.
Finally, clarify any land use restrictions imposed under the lease to determine what activities are permitted on the leased area. Together with financial terms, you can handle these non-financial factors to offer a fair and beneficial setup for all parties to solar leasing.

Comparison Table: Upfronts Payments vs Revenue-Sharing Models
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Protecting your interests in a solar land lease agreement requires understanding potential hazards and strategies for mitigating them. Operational hazards can be effectively controlled by clearly outlining who is responsible for site maintenance and equipment upkeep in the leasing agreement. Defining who will be in charge of ongoing maintenance is crucial to avoiding misunderstandings and guaranteeing the solar project runs well.
Furthermore, clauses about insurance coverage and liability protection must be included to reduce any potential legal and financial concerns that may arise from mishaps or property damage on the leased premises. Economic and market concerns also need to be carefully considered. Energy price fluctuations can have a major effect on revenue-sharing models and the lease arrangement's financial viability.
Financial uncertainty can be mitigated by including clauses that allow for adjustments to revenue-sharing agreements based on market conditions. It is also crucial to take into account advances in solar technology.
Sustaining the project's competitiveness and efficiency during the lease period is ensured by including provisions for equipment updates or improvements as solar technology advances. Through proactive management of these operational, technological, and market risks, you may improve the stability and sustainability of your solar land lease contract.
FAQs
Why do solar companies lease land instead of buying?
- To reduce and control their energy costs.
- To reduce their federal tax liability.
- To invest in an asset with above-average returns.
- To reduce their carbon footprint and protect the environment.
What are the cons of leasing land for solar panels?
- Long-term commitment (20-30 years typically)
- Potential restrictions on land use
- Possible impact on property value
- Uncertainty about future energy prices affecting revenue-sharing models
- Responsibility for site restoration at lease end
- Potential conflicts with local zoning or community opposition
How do solar lease companies make money?
All the solar lease providers listed make their money by financing a solar system for your home and then selling you the solar electricity from the panels. In most cases, the companies promise you will save money on your power bills in the first year a win situation.
There are several ways a solar company can profit and this can include installation, tax credits, investors, selling items that are related to solar energy such as solar fans, payment options, and business location.
What do I need to know before starting a solar company?
- Industry regulations and local zoning laws
- Initial capital requirements and funding sources
- Technical expertise needed for installation and maintenance
- Market demand and competition in your target area
- The supply chain for solar equipment
- Permitting and interconnection processes
- Marketing strategies to attract customers or landowners
Conclusion
Landowners have a rare chance to take part in the renewable energy revolution and maybe earn large financial rewards as the solar energy industry grows. With knowledge of the main factors, requirements, methods of negotiations, and possible hazards related to solar land leasing, you may make choices that optimize the value of your asset.
Keep in mind that every solar land lease agreement is distinct, so what suits one landowner might not be the best for another. When signing a solar land lease deal, always get professional guidance and think about your long-term objectives.






