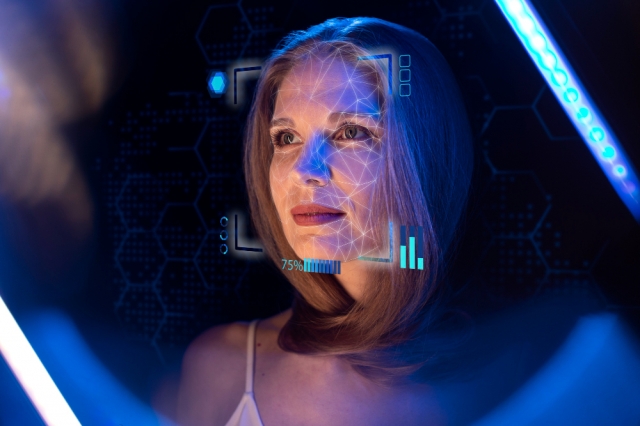
The digital world today has seen a huge rise in artificial intelligence. One exciting area is how AI is used for beauty analysis and aesthetic evaluation. The AI Attractiveness Test combines advanced machine learning, neuroscience, and psychology. It provides users with a tool to see how systems analyze and rate facial features based on beauty standards. This new technology has sparked a lot of discussion about beauty. People are debating if we can measure it objectively and how algorithms shape our views on attractiveness.
Defining the AI Attractiveness Test Paradigm
An AI Attractiveness Test is a digital tool that uses machine learning and computer vision. It evaluates facial features and gives ratings based on set beauty standards and criteria. These systems work by closely examining many facial features. They look at things like symmetry, proportions, skin quality, and how different features are arranged.
The tech behind these evaluative tools has improved a lot in recent years. Modern AI tools for assessing attractiveness use deep convolutional neural networks. These networks are trained on large datasets with millions of facial images. These systems can find and measure many facial landmarks. They include intercanthal distance and mandibular contour curvature. They process this information efficiently, creating detailed attractiveness metrics.
AI systems aim to provide consistent and reliable assessments. AI aims to standardize evaluations, unlike human judgment. Human decisions change based on personal likes, culture, and experiences. It's important to note that these evaluations come from statistical patterns. The AI learns these from training data, which reflect certain cultural and societal beauty standards.
The Scientific Foundations Undergirding AI Beauty Analysis
The epistemological foundation of AI attractiveness testing is anchored in several pivotal scientific principles and theoretical frameworks. Primarily, there exists the construct of facial symmetry, which extensive empirical research has demonstrated correlates significantly with perceived attractiveness across diverse cultural contexts and demographic populations. AI algorithms exhibit particular proficiency in measuring symmetry with mathematical precision, conducting granular analyses of how accurately the left and right facial hemispheres mirror one another.
Secondarily, these computational systems evaluate facial proportions predicated upon classical aesthetic ratios such as the golden ratio (φ ≈ 1.618), which has maintained associations with aesthetic appeal since antiquity. The AI examines whether facial features demonstrate alignment with these mathematical proportions, quantifying aspects including facial width-to-length ratios, orbital positioning, and the spatial relationships between nasal and oral structures.
Furthermore, contemporary AI attractiveness tests incorporate sophisticated analysis of cutaneous texture, clarity, and pigmentation uniformity. Advanced computer vision algorithms possess the capacity to detect and evaluate factors such as epidermal smoothness, chromatic evenness, and the presence of dermatological irregularities or blemishes. The mathematical underpinnings of these systems also incorporate principles from information theory and statistical learning, where algorithms are trained using supervised learning methodologies on millions of facial images annotated with attractiveness ratings.
The Operational Methodology of AI Attractiveness Tests
When an individual engages with an AI Attractiveness Test, the computational process typically unfolds through several sequential stages of increasing analytical complexity. Initially, the user uploads or captures a photographic representation of their facial structure. The AI system subsequently executes facial detection algorithms to localize the face within the digital image and identify critical facial landmarks, potentially including upwards of 68 or more specific anatomical points.
Subsequently, the algorithm calculates the Euclidean distances and angular measurements between these landmarks, constructing a comprehensive mathematical representation of the individual's facial architecture. The system evaluates multiple parameters simultaneously, encompassing facial symmetry metrics through bilateral equilibrium quantification, proportional harmonization assessment against classical aesthetic ratios, feature-specific quality indices for individual morphological elements, dermatological analysis of cutaneous characteristics, and compositional balance evaluation of how disparate features integrate cohesively.
The AI then gives a score or rating. It often includes detailed feedback on specific facial features and how they affect the overall score. Advanced platforms provide personalized recommendations or insights. They show which morphological features matter most for the overall evaluation.
Exploring PixNova AI's Advanced Attractiveness Test
If you want to explore AI beauty analysis, try PixNova AI. They offer a cutting-edge AI Attractiveness Test that showcases top-tier technology. PixNova AI is a top platform for online image generation, editing, and interactive services. These include AI-powered face-swapping, image creation, one-click outfit changes, AI virtual character interactions, and more.
The platform's attractiveness test stands out with its smart algorithm. It offers detailed analysis while keeping a respectful and positive approach. Users often praise the tool for providing useful numbers and helpful insights about their facial shape. It's both fun and informative.
The Cultural Relativism of Beauty Standards
A key point in AI attractiveness tests is how beauty standards differ across cultures. Attractiveness can vary greatly between cultures. What one culture finds appealing might not be the same in another. For example, some facial features are prized in East Asian beauty standards. In contrast, different traits are valued in Western and African styles.
AI systems only reflect the features of the data they're trained on. This means they can unintentionally carry and reinforce certain cultural biases and dominant aesthetics. Ethically responsible AI attractiveness tests recognize their limits. They either train on diverse datasets or provide culturally specific assessments for different demographic groups. Beauty standards vary widely. They include not just facial features but also skin tone, hair texture, and age. This shows that beauty is a social construct.
Psychological Ramifications and Considerations
AI attractiveness tests can be fun and boost confidence for some users. However, it's important to view them with the right mindset and a critical eye. Beauty is subjective and complex. No algorithm can fully capture what makes someone attractive. It includes personality traits, charm, confidence, and many other intangible qualities.
Mental health experts warn that relying too much on outside approval—like from algorithms or people—can harm self-esteem and mental health. These tests are more like fun tools or conversation starters. They shouldn't be seen as final judgments of your value or how likable you are. For people with body dysmorphic disorder or self-image issues, these tests might not be suitable. The scores depend on limited criteria and don't capture the full range of human beauty.
Technological Evolution and Practical Applications
The domain of AI-powered facial analysis continues to undergo rapid evolutionary development. Contemporary platforms now use advanced technologies. They include 3D facial mapping for better accuracy. They can also detect age and emotions to see how expressions affect perceived attractiveness. Additionally, they offer personalized style recommendations based on a person's facial shape. Future developments may include facial animation dynamics analysis and microexpression detection capabilities.
Beyond entertainment, these technologies possess substantive applications across various industrial sectors. The cosmetics industry leverages facial analysis for product recommendations and virtual try-on functionalities. Plastic surgeons employ advanced facial analysis for treatment planning. The entertainment industry uses AI tools to assess photogenic qualities. In fashion, facial analysis helps select models and offers personalized styling tips.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Implementation
Attractiveness tests, like any AI that judges human traits, raise important ethical issues. Developers must be clear about how algorithms work. They should not support harmful beauty standards or discrimination. It's important to show results in a helpful way and include disclaimers about any limits. Also, they need to keep user privacy safe with strong security measures.
Conclusion
The AI Attractiveness Test is a big step in AI and computer vision. It shows how powerful today's machine learning systems can be. These tools offer a fascinating look at how computers learn to recognize and assess patterns in human facial features. People are drawn to PixNova AI for many reasons. Some are curious about technology, while others seek entertainment. Many want to see how AI views beauty standards. This platform makes it easy to explore the mix of technology and art. It's important to know that true attractiveness goes far beyond what any algorithm can measure. Confidence, compassion, authenticity, and character contribute immeasurably to interpersonal perception. AI attractiveness tests can be fun and informative. However, they should complement your self-perception, not define it. Beauty is deeply personal and varies greatly from person to person. It is subjective and diverse. No artificial intelligence can fully capture or measure these qualities.