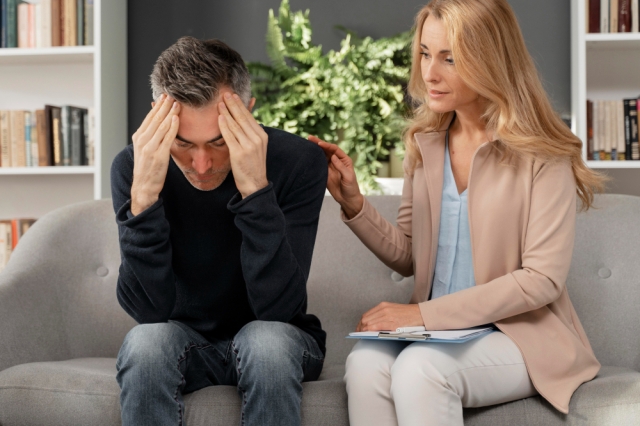
As we delve into the complex realm of adulthood, marked by diverse experiences and ongoing personal development, it becomes evident that challenges in managing behavior are not exclusive to childhood. This blog aims to shed light on prevalent behavior disorders in adults, offering insights into their characteristics, underlying causes, and avenues for meaningful support and intervention.
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
While commonly associated with childhood, ADHD can persist into adulthood, posing unique challenges. Adults grappling with ADHD may find it difficult to focus, control impulses, and regulate energy levels. Symptoms encompass inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. A blend of genetic factors, brain structure, and environmental influences contributes to ADHD. A comprehensive approach involving behavioral therapy and medication is instrumental in enhancing the functioning of adults with ADHD.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder, a lifelong neurodevelopmental condition, affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. Adults with ASD may encounter challenges in social interactions, exhibit repetitive behaviors, and display intense interests. Autism treatment for adults often includes behavioral therapy, social skills training, and creating inclusive environments in workplaces and communities.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
The manifestation of Oppositional Defiant Disorder is not confined to childhood; adults can exhibit persistent patterns of disobedient, defiant, and hostile behavior toward authority figures. This may involve arguments, defiance, and irritability. Workplace conflicts, interpersonal issues, or underlying mental health concerns can contribute to the development of ODD in adults. Interventions often encompass individual counseling, conflict resolution strategies, and fostering a supportive environment.
Conduct Disorder (CD)
While traditionally linked with adolescence, Conduct Disorder can extend into adulthood, characterized by persistent patterns of aggressive behavior, rule violations, and a disregard for the rights of others. Adults with CD may engage in activities such as theft, vandalism, and physical aggression. A complex interplay of biological, genetic, and environmental factors influences the development of CD. Treatment may require a combination of individual therapy, group therapy, and, in some cases, medication to address the underlying issues.
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can persist or emerge in adulthood, significantly impacting behavior and daily functioning. Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder are prevalent forms. Adults grappling with anxiety may experience excessive worrying, fearfulness, and physical symptoms like headaches or stomachaches. Interventions, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness techniques, and medication, are effective in managing anxiety disorders and fostering a sense of well-being in adults.
Depression and Mood Disorders
Depression and mood disorders can deeply affect behavior in adulthood. Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in once-enjoyable activities can manifest in behavioral changes. Adults may become withdrawn, irritable, or exhibit changes in sleep and appetite. Psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications are integral components of managing depression and mood disorders in adults, allowing for a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding behavior disorders in adulthood is pivotal for fostering empathy and providing timely, targeted interventions. Every adult's journey is unique, and behavior disorders may stem from a complex interplay of genetic, biological, and environmental factors. By identifying signs and embracing a collaborative approach that involves professional assistance and support networks, we can empower adults to navigate the challenges associated with behavior disorders. Early and comprehensive intervention significantly improves outcomes, enabling adults to lead fulfilling lives marked by resilience and success.